Impacts of Hurricanes on Barbados
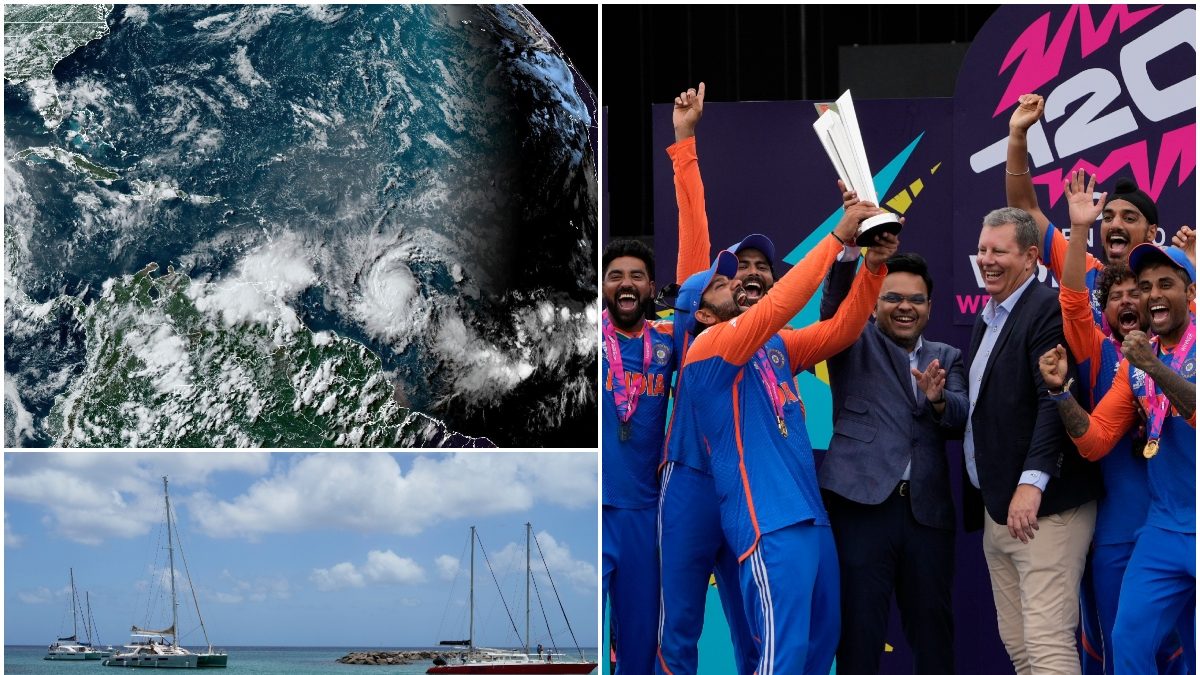

Barbados hurricane – Barbados, an eastern Caribbean island nation, is periodically impacted by tropical cyclones, particularly hurricanes. These powerful storms pose significant threats to the island’s economy, society, and environment.
Barbados recently experienced a devastating hurricane. Meteorologists use a variety of tools to predict the path of hurricanes, including spaghetti models. These models simulate the possible paths of a hurricane based on different initial conditions. By looking at the ensemble of all the spaghetti models, meteorologists can get a better idea of the most likely path of the hurricane.
This information can help them issue timely warnings and evacuations, which can save lives.
Historically, Barbados has experienced numerous hurricanes, with some leaving devastating impacts. In 1780, the Great Hurricane of 1780 claimed over 4,000 lives and destroyed much of the island’s infrastructure. More recently, Hurricane Janet in 1955 caused widespread damage, leaving over 100,000 people homeless. Hurricane Ivan in 2004 also had significant impacts, causing extensive flooding and power outages.
Dis hurricane weh hit Barbados did bad bad. But we strong and we a rebuild. We a get help from all over, including from beryl barbados. We thankful for all di support and we know we will come out stronger dan ever.
Economic Impacts
- Hurricanes can cause extensive damage to infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. This can disrupt transportation, communication, and economic activity.
- The tourism sector, a major contributor to Barbados’ economy, can be severely affected by hurricanes. Storm damage to hotels, resorts, and other tourist attractions can lead to a decline in visitor arrivals and revenue.
- Hurricanes can also damage crops and livestock, leading to losses in the agricultural sector.
Social Impacts
- Hurricanes can cause widespread displacement and homelessness. People may lose their homes and belongings, and access to essential services such as healthcare and education may be disrupted.
- Hurricanes can also lead to psychological trauma and stress for those who experience the storms.
- The disruption of infrastructure and services can also affect the elderly, children, and other vulnerable populations.
Environmental Impacts
- Hurricanes can cause significant damage to coastal ecosystems, including coral reefs and mangrove forests. These ecosystems provide important ecosystem services, such as protecting the coastline from erosion and providing habitat for marine life.
- Hurricanes can also lead to flooding, which can damage freshwater resources and contaminate drinking water.
- The high winds and storm surges associated with hurricanes can also cause erosion and damage to beaches and coastal infrastructure.
Vulnerabilities and Resilience
Barbados’ vulnerabilities to hurricanes are influenced by factors such as its geographic location, coastal exposure, and socio-economic conditions. The island’s low-lying coastal areas are particularly vulnerable to storm surges and flooding.
Barbados has implemented various measures to enhance its resilience to hurricanes, including strengthening building codes, improving early warning systems, and investing in disaster preparedness and response plans. The island has also received support from international organizations, such as the World Bank and the United Nations, in its efforts to reduce hurricane risk.
Hurricane Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies
To effectively prepare for and mitigate the impacts of hurricanes in Barbados, a collaborative approach involving government agencies, organizations, and individuals is crucial. This comprehensive strategy encompasses early warning systems, evacuation plans, disaster response protocols, building codes, land use planning, and community engagement.
Role of Government Agencies, Organizations, and Individuals
Government agencies, such as the Barbados Meteorological Services and the Department of Emergency Management, play a vital role in hurricane preparedness. They provide early warnings, issue evacuation orders, and coordinate disaster response efforts. Organizations, including the Barbados Red Cross and the Salvation Army, assist with evacuation, shelter, and relief operations.
Individuals also have a responsibility to prepare for hurricanes. This includes developing a family emergency plan, securing their homes, and stocking up on essential supplies.
Early Warning Systems, Evacuation Plans, and Disaster Response Protocols
Barbados has an advanced early warning system that provides timely alerts to residents. The system utilizes weather satellites, radar, and other technologies to monitor and predict hurricane activity. Evacuation plans are in place to ensure the safe and orderly movement of people from vulnerable areas.
Disaster response protocols Artikel the actions to be taken before, during, and after a hurricane. These protocols include the activation of emergency response teams, the establishment of shelters, and the provision of medical assistance.
Best Practices for Hurricane Mitigation
Hurricane mitigation measures aim to reduce the vulnerability of communities to hurricanes. Building codes in Barbados are designed to withstand high winds and storm surges. Land use planning regulations restrict development in flood-prone areas and encourage the use of natural buffers, such as mangroves, to protect coastal communities.
Community engagement is essential for effective hurricane mitigation. Public education campaigns raise awareness about hurricane risks and promote preparedness measures. Community organizations work with residents to identify vulnerable areas and develop local disaster response plans.
Climate Change and Hurricane Impacts: Barbados Hurricane
Climate change poses significant threats to Barbados and its vulnerability to hurricanes. Rising sea levels, intensifying storm surges, and altered precipitation patterns are among the key concerns.
Sea Level Rise and Storm Surge
As global temperatures increase, the thermal expansion of ocean waters and the melting of glaciers and ice caps contribute to sea level rise. Higher sea levels lead to increased coastal erosion, flooding, and storm surge during hurricanes. Storm surge, the rise in sea level caused by hurricane winds, can inundate low-lying coastal areas, causing severe damage to infrastructure and property.
Precipitation Patterns, Barbados hurricane
Climate change is also projected to alter precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent and intense rainfall events. Heavier rainfall during hurricanes can exacerbate flooding, landslides, and infrastructure damage. Increased rainfall intensity can also lead to freshwater contamination and disrupt water resources.
Recommendations for Adaptation and Mitigation
To adapt to and mitigate the potential impacts of climate change on hurricane risks in Barbados, several measures can be implemented:
- Coastal protection and adaptation: Implement measures such as seawalls, breakwaters, and mangrove restoration to protect coastal areas from erosion and storm surge.
- Land use planning and zoning: Restrict development in high-risk coastal areas and establish setbacks to reduce exposure to flooding and storm damage.
- Improved infrastructure: Design and build infrastructure to withstand stronger winds and higher sea levels, including hurricane-resistant buildings, bridges, and roads.
- Water management: Implement measures to manage stormwater runoff and reduce flooding, such as green infrastructure, retention ponds, and improved drainage systems.
- Climate change education and awareness: Raise awareness about the impacts of climate change on hurricanes and encourage public participation in mitigation and adaptation efforts.